Introduction
The black Truffle Shelf Life (Tuber melanosporum), often referred to as the "black diamond" of gastronomy, is a highly prized culinary delicacy known for its intense aroma and unique flavor. Fresh truffles are seasonal and perishable, making their availability limited. To extend their shelf life and ensure year-round access, freezing has emerged as a popular preservation method. This report delves into the intricacies of frozen black truffles, examining their preservation techniques, quality retention, and culinary uses.
1. The Black Truffle: A Brief Overview
Black truffles are subterranean fungi that grow in symbiotic relationships with the roots of certain trees, such as oaks and hazelnuts. They are primarily harvested in regions like France, Spain, and Italy. Their distinct earthy, musky aroma and umami-rich flavor make them a staple in haute cuisine. However, their short shelf life—typically 1-2 weeks when fresh—poses a significant challenge for chefs and food enthusiasts.
2. Preservation Methods: Why Freezing?
Freezing is one of the most effective methods to preserve black truffles, as it slows down enzymatic and microbial degradation. Unlike drying or canning, freezing retains the truffle's texture and volatile compounds, which are critical for its flavor and aroma. The process involves:
2.1 Preparation for Freezing
- Cleaning: Truffles are gently brushed to remove soil and debris. Washing with water is avoided to prevent moisture absorption.
2.2 Freezing Techniques
- Flash Freezing: This method involves rapid freezing at ultra-low temperatures (-30°C or lower) to minimize ice crystal formation, which can damage cellular structure.
3. Quality Assessment of Frozen Black Truffles
The quality of frozen black truffles is evaluated based on aroma, flavor, texture, and visual appearance. Studies have shown that:
3.1 Aroma and Flavor Retention
Freezing preserves most of the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) responsible for the truffle's aroma, such as dimethyl sulfide and 2,4-dithiapentane. However, some degradation occurs over extended storage periods (beyond 6 months).
3.2 Texture
While freezing can cause slight textural changes due to ice crystal formation, vacuum-sealed truffles maintain a firm consistency comparable to fresh truffles when thawed properly.
3.3 Visual Quality
Frozen truffles retain their dark, knobby exterior, though prolonged freezing may lead to minor discoloration.
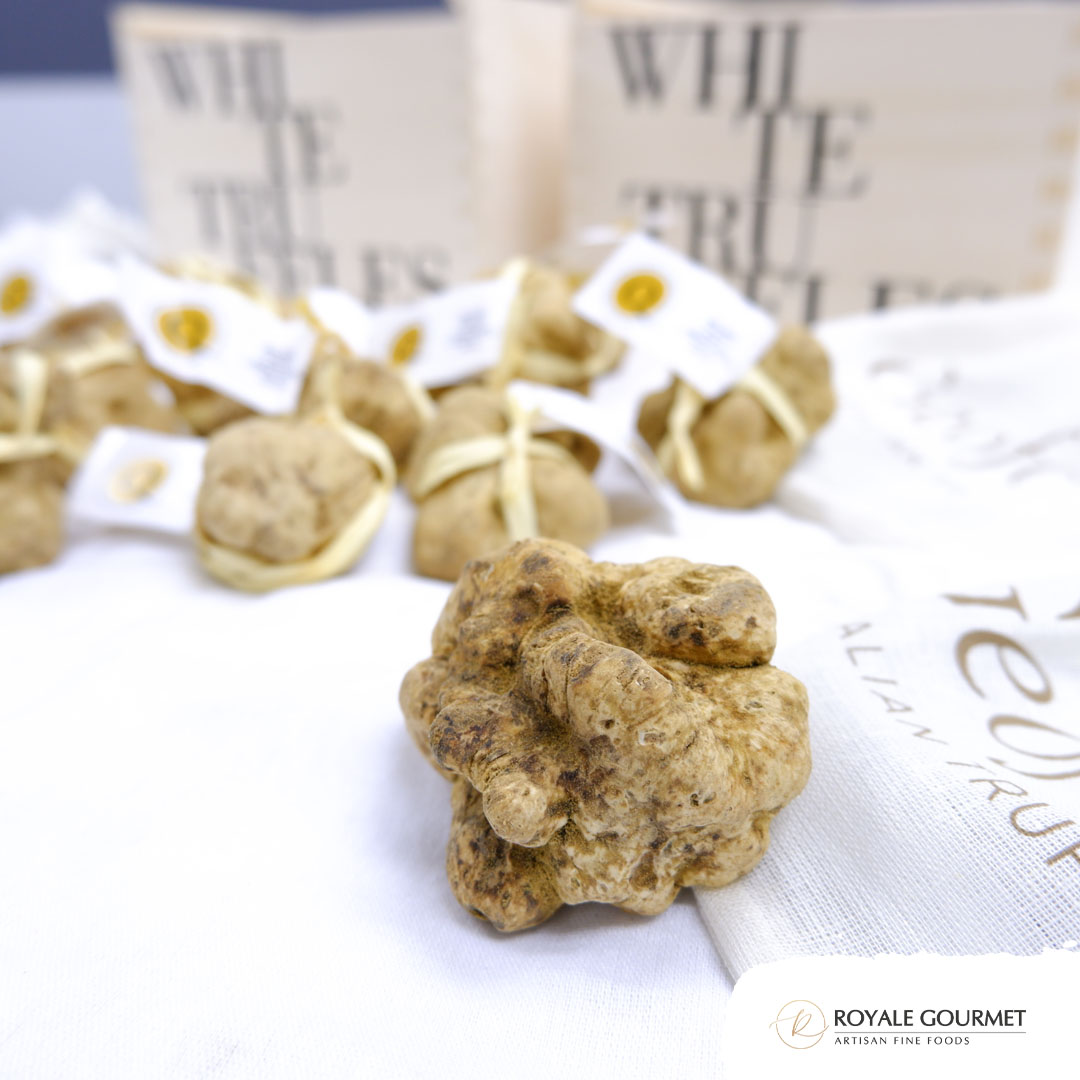

4. Thawing and Culinary Applications
Proper thawing is crucial to maximize the quality of frozen black truffles. The recommended method is gradual thawing in a refrigerator (4°C) for 12-24 hours. Avoid microwaving or rapid thawing, as this can exacerbate textural loss.
4.1 Culinary Uses
Frozen black truffles are versatile and can be used in:
- Sauces and Soups: Infused into creamy sauces or broths to enhance depth of flavor.
5. Advantages and Limitations of Frozen Black Truffles
5.1 Advantages
- Extended Shelf Life: Frozen truffles can last up to 12 months without significant quality loss.
5.2 Limitations
- Slight Quality Compromise: Aroma and texture may not match peak freshness.
6. Market Trends and Consumer Perception
The demand for frozen black truffles has surged, particularly among professional kitchens and gourmet food retailers. Consumers appreciate their accessibility, though purists still prefer fresh truffles for their unparalleled quality. Innovations in freezing technology, such as cryofreezing, aim to bridge this gap further.
7. Conclusion
Frozen black truffles offer a practical solution to the challenges of seasonality and perishability. While they may not entirely replicate the experience of fresh truffles, their quality, when preserved correctly, comes remarkably close. As freezing techniques advance, frozen truffles are poised to become a staple in both professional and home kitchens, democratizing access to this luxurious ingredient.
8. References
(Note: Include relevant studies, culinary guides, and industry reports here in a formal citation format.)